The constellation "Little Dog" is quite unobtrusive and to help you find it, look for its "shoulder star", "Betelgeuse" of the constellation Orion. The constellation "Little Dog" is one of the 48 which Ptolemy described in early Greek astronomy. In ancient Greek the name of the main star "Procyon" means "before the dog". This is an indication that the Procyon called it the "Dog Star".
Shape and position:
The constellation "Little Dog" is an unexceptional and small constellation. The observer finds it south of the constellation "Twins". Apart from the inner part of the Antarctica, the "Little Dog" is visible all year round from the entire world.
Right ascension: 7h 8h 6m to 11m
Declination: +0 ° to +13 °
Brightest star: Prokyon (α Canis Minoris)
Mythology:
In Greek mythology, Dionysus is the god of intoxication, and taught the farmers Icarius how to press grapes. Icarius offered the same to the shepherds that enjoyed plenty of it. In their rush they thought Icarius had poisoned them and so they had to kill him. Erigone, the daughter of Icarius, searched for her father with her little dog. The shepherds were punished and the "Little Dog" got his pride of place in the firmament. In another version of the origin of the constellation "Little Dog" is the doggy companion of the hunter Orion.
Best season for observation: Winter
Neighbouring constellations: Unicorn, Twins, Crab, Water snake
Buy a Star Blog
-
Star Sign Little Dog
-
Star Sign Fishes
Pisces, also known as 'The Fishes', is one of the most singular and interesting constellations which can be viewed from Earth. Pisces is a very unusual constellation. As one of the signs of the Zodiac, it is situated on the ecliptic line, or the level of planetary orbits. This means that the Sun, Moon and planets of our Solar System appear to move through the constellation on occasions when it is viewed from Earth.
Shape and position: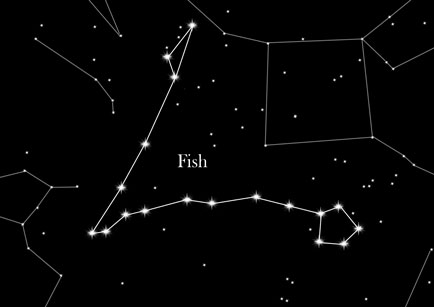
Pisces is a very large constellation in terms of the area in the night sky it covers. Despite its large area though, it is not easy to see, especially in urban areas. Its brightest star, Alrischa, has a magnitude of just 3.5. Stargazers can use the constellation Pegasus, known as the Autumn Triangle, to help them locate Pisces, as this is situated nearby. With its long shape, Pisces often reminds contemporary observers of a scooter.
Right ascension: 22h 51m to 2h 6m
Declination: -6 to +34°
Brightest star: Alpha Piscium (Alrischa)
Mythology:
Greek mythology tells of Zeus killing his father Kronos, and waging war against the Earth Goddess, Gaia. Zeus imprisoned Gaia's children, the Titans, and as a result the Earth Goddess created the monster Typhon to wreak vengeance on Zeus and the gods of Olympus. This monster had a hundred dragon heads and was so fearsome that even the goddess Aphrodite was overcome with fear. She threw herself into the River Euphrates to escape, and there was rescued by two fish. As a tribute to the heroic deed of the fish, the goddess immortalized them in the night sky as Pisces. Other legends insist that the constellation is the skeleton of the sea monster which Perseus defeated to save Princess Andromeda.
Astrological significance: Pisces is a sign of the Zodiac, and anyone born February 21 to March 20 will have The Fish as their astrological sign. Pisceans are generally regarded as being social and lovable, though also perhaps a little dreamy and occasionally chaotic. They are often talented artists who possess a shy charm. The element of Pisces is water.
Best season for observation: Fall
Neighbouring constellations: Andromeda, Triangle, Pegasus, Aquarius, Whale, Ram -
Star Sign Unicorn
The constellation "Unicorn" is to be found south of the celestial equator and is relatively inconspicuous. However, benefited from the Unicorn during the bright band of the Milky Way, which crosses the unicorn. Many nebulae and other objects of observation make the Unicorn very interesting for astronomers.
Shape and position: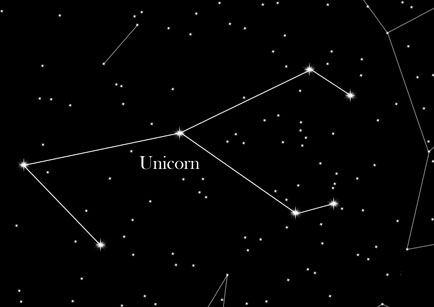
The Unicorn is found east of the constellation Orion and north of a bright star in Constellation "Big Dog". The constellation only contains two stars with magnitude 4, but are beautiful objects from the same observation bright band of our Milky Way. Thus, for example of the open cluster M50 very admirable and well-known "Rosette Nebula". The head of the Unicorn is made up by a triangle and one can also see the front half of the front hooves.
Right ascension: 5h 55m to 8h 11m
Declination: -11 to +11 degrees
Brightest star: Beta Monocerotis
Mythology:
The unicorn is not one of the 48 ancient classical constellations, so it has no mythological background in which the gods are said to have denied fighting or won victories.
Best season for observation: Winter
Neighbouring constellations: Little Dog, Great Bear, Twins, Orion, Wolf, Water snake -
Star Sign Charioteer
The Charioteer is one of the 48 constellations described by Ptolemy. In about 13,000 years the carter will mark the celestial equator. Due to its expansion and position, the Charioteer is an easily recognizable constellation. The Babylonians came up with the current name of Auriga. Auriga means "charioteer" or "Helmsman" in latin.
Shape and position: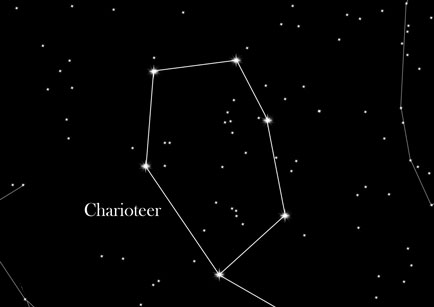
With just one star in the neighboring constellation, Taurus "borrowed" a star in the Charioteer which is a almost regular pentagon. Its main star, Capella, is the third brightest star in the Northern sky. The southernmost star Alnath, which completed the pentagon, was earlier known as γ Aurigae in the constellation Auriga. After determining the constellation boundaries in the "International Astronomical Union" (IAU), this star is today, however, in the constellation Taurus. Through the center of the constellation goes the starry band of the Milky Way. That's why there are some interesting items, such as some star clusters and bright nebulas to observe.
Right ascension: 4h 35m to 7h 30m
Declination: +28 to +56 degrees
Brightest star: Capella (Alpha Aurigae)
Mythology:
In the Greek mythology, the son of blacksmith Hephaestus, named Erichthonius, is associated with the constellation Auriga. Erichthonius was the creator of the quadriga, a four-horse chariot used in battles. When he beat Amphictyon in battle, he became the King of Athens. This was in large thanks to his intelligence, and Zeus rewarded him after he died with a place in the sky.
Best season for observation: Autumn
Neighbouring constellations: Giraffe, Perseus, Bull, Twins, Lynx -
Star Sign The Little Bear
Also known as the 'Little Dipper', the Little Bear is one of the most important constellations in the sky to astronomers. The Little Bear (Ursa Minor in Latin, or 'smaller bear') is a constellation of the Northern sky. Visible from Europe throughout the year, it is occasionally referred to as the 'Little Dipper'. The main star of this constellation is Polaris, one of the most important stars in the sky to astronomers. All other celestial bodies seem to turn throughout a day using this star as a pivot. Polaris is also given a significant role in the legends of the Indian Vedas, being the leader of a group of gods.
Shape and position:
The Little Bear is similar in shape to the Great Bear, sometimes referred to as the 'Big Dipper'. This is why Ursa Minor is sometimes called the 'Little Dipper'. Unlike the Big Dipper, the 'handle' of the Little Dipper is not straight, but rather is bent upwards. The main star of the constellation, Polaris, remains fixed in its position in the night sky. The altitude of the star's position in the north corresponds to the viewer's latitude.
Right ascension: 0h 0m to 24h 00m
Declination: +65 to 90 degrees
Brightest star: Alpha Ursae Minoris (Polaris or Northern star)
Mythology:
Callisto was a beautiful nymph who attracted Zeus. She later gave birth to the god's son Arcas. Hera, the wife of Zeus, transformed Callisto into a bear. Years later, when Arcas was hunting in the woods, Hera made sure that Callisto encountered her son. Arcas was about to unintentionally kill his mother, when Zeus intervened. The god placed Callisto in the heavens as the Great Bear, and later made sure that Arcas joined her as the Little Bear.
Best season for observation: Year-round, with the best time in spring
Neighbouring constellations: Cassiopeia, The Dragon, The Giraffe, Great Bear, Cepheus


